Table of Contents
How To Calculate Hours Worked? Formula and Examples
Calculating work hours expended on a project is paramount for a business, as it yields critical insights into project efficiency, resource allocation, and financial forecasting. It facilitates meticulous project planning, enabling more precise estimation of man-hours and effort for future undertakings.
Time tracking is instrumental in identifying workflow bottlenecks, thereby ensuring adherence to project timelines and optimizing client satisfaction. Additionally, it supports performance metrics analysis, pinpointing areas for enhancement and incentivizing productivity.
What’s The Easiest Way To Calculate Hours Worked? Online Timesheet Software
Use an online timesheet software like Avaza.
Online timesheet software allows businesses to track and manage employee working hours accurately. It simplifies time tracking, invoicing, and project management through an intuitive interface for logging accurate work hours.
Employees can easily log their time, while employers/clients can review and approve timesheets efficiently. This software simplifies hour calculations, minimizing mistakes and saving time over manual methods (to be discussed later).
Key Features:
- Automated Time Tracking
- Timesheet Approvals
- Flexible Timesheet Entry
- Real-Time Reporting
- Multi-Device Access
- Billable and Non-Billable Hours Tracking
- Overtime Tracking
- Timesheet Reminders
- Integration with Accounting Systems
- Customizable Timesheet Fields
How Does Avaza Solve Common Work-Hour Calculation Problems?
Here’s how Avaza addresses common challenges businesses face with calculating work hours:
1. Automatic and Accurate Time Tracking
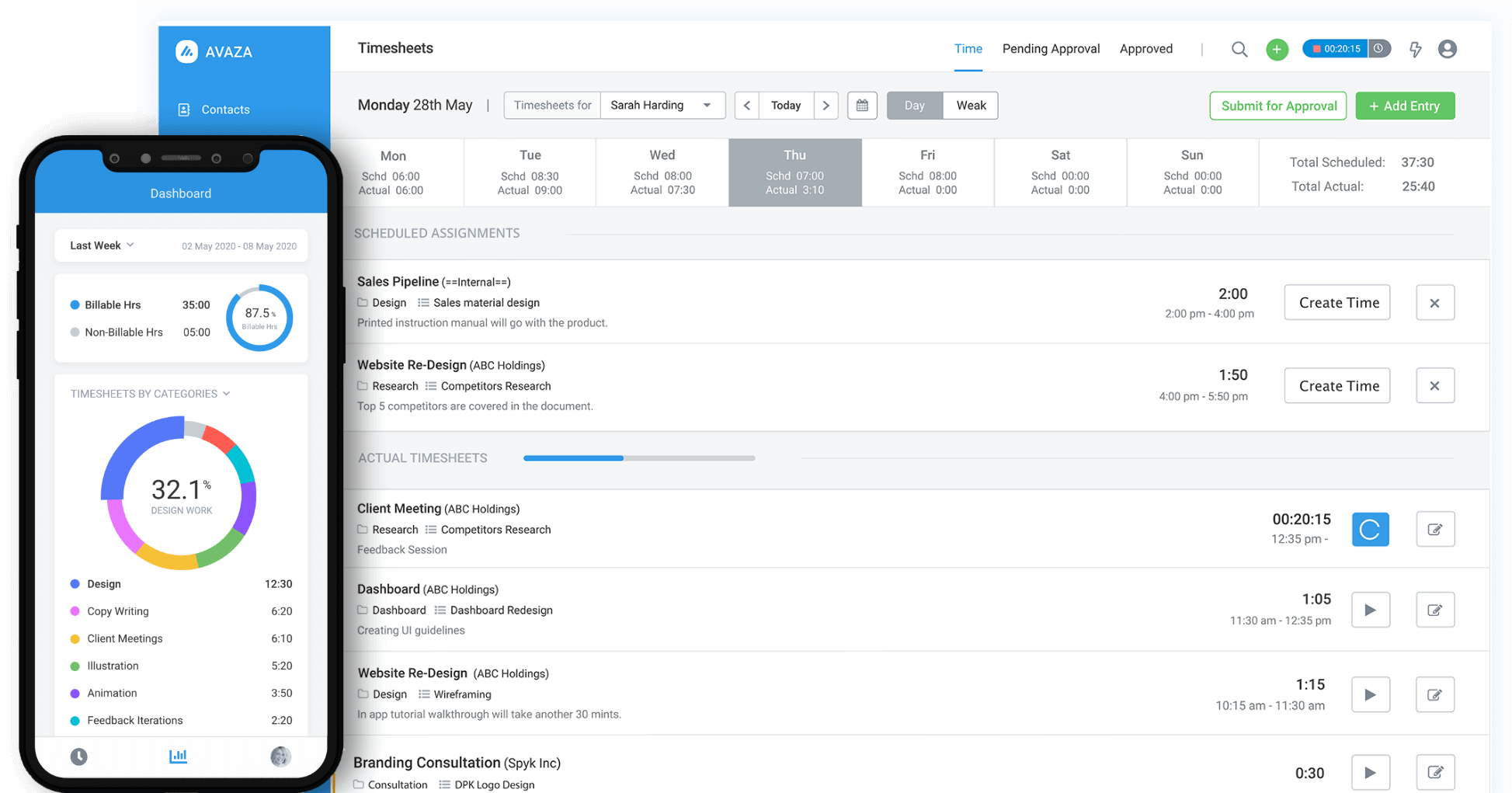
Avaza offers one-click time tracking, allowing users to start and stop timers with a single click. This ease of use ensures that time is recorded precisely without manual input errors.
Avaza supports multiple methods for tracking time, including timers, manual entry, and integration with other tools, providing flexibility depending on user needs.
It effectively differentiates between billable and non-billable hours, making it easier to categorize and invoice clients accurately. This separation helps in managing project budgets and ensures transparency in billing.
2. Seamless Integration with Accounting Systems

Avaza integrates seamlessly with accounting systems (like Xero and QuickBooks), streamlining the payment process. Its project management tools are built into the platform, allowing for efficient time and expense tracking across all projects.
This integration supports transparent billing by aligning project hours with client invoices.
Avaza simplifies sending time-based invoices by automatically generating them based on the tracked time and billable rates, reducing administrative overhead.
This seamless process ensures businesses can manage payroll and invoicing more efficiently without juggling separate systems.
3. Real-Time Reporting and Analytics
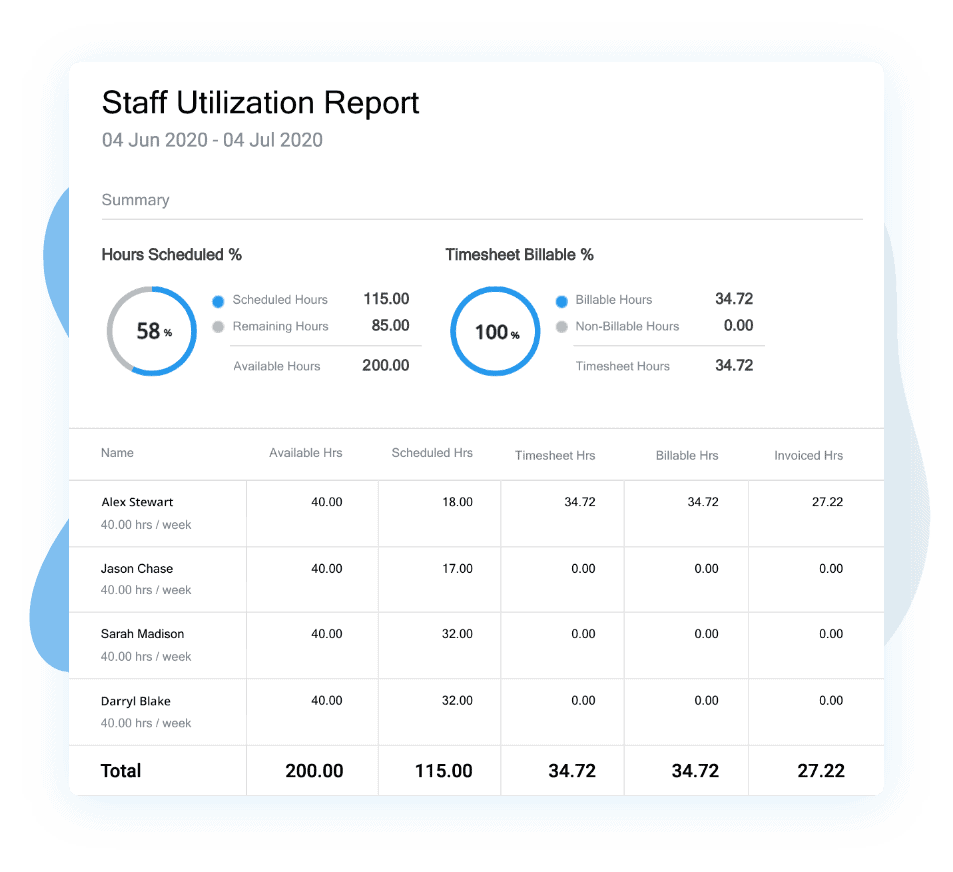
Avaza provides powerful real-time reporting and analytics tools that offer valuable insights into time management and project progress.
Users can access insightful reports that detail hours worked, project costs, and more, helping to make informed business decisions. The platform enables you to schedule reports to run automatically at designated intervals, keeping your data up-to-date.
Avaza’s suite of reports is extensive, covering various aspects of project performance and time tracking. These reports aid in evaluating productivity and optimizing workflows.
How to Implement Online Timesheet Software in Your Business?
Here’s how to ensure a smooth transition, from choosing the right online timesheet software to optimizing its use for your business needs.
1. Choosing the Right Software for Your Needs
When choosing an online timesheet software, prioritize features that meet your business needs. Seek out software with time-tracking capabilities, automated calculations, and smooth integration with accounting systems.
User-friendly interfaces and mobile access are essential for ease of use.
Evaluate top providers by comparing their features, customer support, and pricing models. Choose software that meets your current needs and can scale as your business grows.
2. Setting Up and Integrating the Software
Begin by setting up the software according to the vendor’s instructions. This typically involves configuring user accounts, defining timesheet categories, and setting up approval workflows.
Ensure the software seamlessly connects with your current accounting system.
This integration helps maintain data consistency and streamline processes. Test the integration thoroughly to resolve any issues before fully deploying the system.
Proper setup and integration are essential for maximizing the efficiency and accuracy of time tracking.
3. Training Your Team and Ensuring Adoption
Effective onboarding is key to successful software implementation. To familiarize your team with the new system, provide comprehensive training sessions, offer hands-on practice, and create user guides to address common questions.
Encourage adoption by highlighting the software’s benefits, such as improved accuracy in time tracking and simplified invoicing processes. Solicit feedback from users to identify any challenges and address them promptly.
Regular check-ins and support can also maintain high levels of engagement and usage.
4. Monitoring and Optimizing Usage
Review how the software is being used within your organization regularly. Look for patterns or issues that may indicate areas for improvement. Use built-in analytics to gain insights into time-tracking accuracy and employee productivity.
Based on these insights, adjust workflows or settings to enhance efficiency. Periodic software updates, based on user feedback and new feature releases, will help keep the system optimized and aligned with your business needs.
💡 What Are Project-Based Work Hours?Project work hours refer to the total time team members spend on tasks and activities related to a specific project. These hours cover all project lifecycle phases, including planning, execution, monitoring, and closing. Accurate tracking of project work hours is essential for effective project management, as it helps in resource allocation, budget management, and meeting deadlines. Tracking project work hours provides insights into the time dedicated to various tasks and which activities consume more resources. This information is crucial for identifying bottlenecks, optimizing workflows, and improving productivity. Additionally, it allows project managers to make informed decisions about workload distribution, ensuring that team members are adequately supported and utilized. Project work hours can be recorded manually or through time tracking software. Tools like Avaza’s online timesheet software offer automated tracking, real-time reporting, and seamless integration with accounting systems. This facilitates a more accurate and efficient way to manage project hours, ultimately leading to better project outcomes. |
What Are Some Common Methods To Track Hours Worked?
Various methods exist to accurately track hours worked, each with its advantages and limitations.
1. Handwritten Timecards
Process:
- Employees manually record their start and end times each day.
- Timecards are filled out by hand, with hours worked noted in each section.
Limitations:
- This method is straightforward but susceptible to inaccuracies due to human error.
- Compiling and verifying timecard data is time-consuming and prone to mistakes.
- Managing and storing handwritten timecards can be challenging, particularly for businesses with many employees.
2. Excel or Google Spreadsheets
Process:
- Employees enter work hours into predefined cells within a spreadsheet.
- Spreadsheets use formulas to automatically calculate total hours, overtime, and other variables.
- This method is more organized than handwritten timecards and helps reduce calculation errors.
Limitations:
- Requires manual data entry and regular updates, which can lead to human errors.
- Does not provide real-time tracking and can become cumbersome if the spreadsheet is not carefully managed.
3. Online Timesheet Software
Process:
- Provides a digital platform for tracking work hours via a web interface.
- Employees log their work hours directly into the software, which automatically records and calculates the data.
Benefits:
- It offers project-based time tracking, reduces manual errors, and streamlines administrative tasks.
- Integrates with accounting software systems for accurate and efficient invoicing.
- Supports mobile access, allowing employees to log hours from various devices and locations.
- Enhances accuracy, efficiency, and flexibility in tracking work hours.
How To Calculate Total Hours Worked? Step-By-Step Manual Process
Here’s a straightforward guide to calculate hours worked step by step.
1. Determine the start and the end time
Document the exact time an employee begins and ends their shift. For example, if an employee starts at 9:00 AM and finishes at 5:30 PM, record these times accurately.
This can be done using punch cards, online timesheets, or digital time clocks.
2. Convert the time to military time (24 hours)
Use military time (24-hour format) to simplify calculations. The AM times will remain the same. However, you only need to convert the PM time. You can convert PM times by adding 12 to each hour.
For example, 3:00 PM becomes 15:00 (i.e., 3+12=15), and 8:45 PM becomes 20:45 (i.e., 8+12=20).
3. Transform the minutes into decimals
Convert hours and minutes into a decimal format for more straightforward calculations. Divide minutes by 60. For instance, if an employee’s end time is 17:30, divide 30 by 60 to get 0.5. Thus, the end time in decimal format is 17.5.
Example: 7:45 becomes 7.75 hours, and 17:00 remains 17.00 hours.
4. Subtract the start time from the end time
Now you need to subtract the start time from the end time.
For instance, if the start time is 7.75 hours and the end time is 17.00 hours, calculate 17.00 – 7.75 = 9.25 hours.
5. Subtract the unpaid time taken for breaks
Deduct any unpaid break time. Convert the break time to decimal format using the same method. For example, a 30-minute break is 0.5 hours. If the total hours worked were 9.25 and the break was 0.5 hours, subtract 0.5 from 9.25 to get 8.75 hours worked.
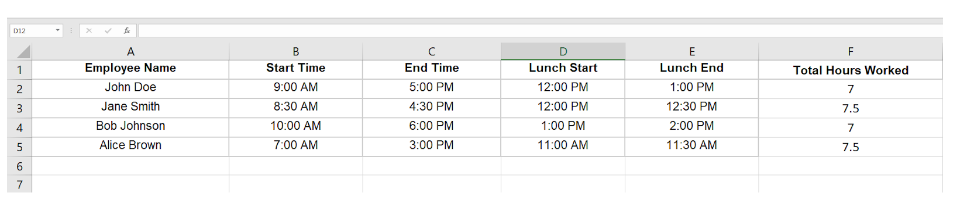
How do you calculate hours worked in Excel/Google Sheets (with lunch break)? Manually Calculating Work Hours
To calculate hours worked in Excel or Google Sheets (manually), including lunch breaks, follow these steps below:
Input Data:
- Column A: Employee Name
- Column B: Start Time
- Column C: End Time
- Column D: Lunch Break Start Time
- Column E: Lunch Break End Time
- Column F: Total Hours Worked
Format Cells for Time:
- Select the cells in columns B, C, D, and E.
- Right-click and choose “Format Cells.”
- Select “Time” and choose a suitable time format (e.g., 1:30 PM).
Enter Data:
- Enter the employee name in Column A.
- Enter the start time, end time, lunch break start time, and lunch break end time in Columns B, C, D, and E, respectively.
Calculate Total Work Hours:
In Column F, use the following formula to calculate the total work hours minus the lunch break:
=((C2-B2) – (E2-D2))*24 |
Explanation:
- (C2 – B2): Calculates the total time from start to end.
- (E2 – D2): Subtracts the lunch break duration.
- Multiplying by 24 converts the result from a fraction of a day to hours.
Copy Formula for All Rows:
Drag the formula in Column F down to apply it to all rows with data.
Format Total Hours Worked:
- Select the cells in Column F.
- Right-click and choose “Format Cells.”
- Select “Number” or “Custom” and choose a format that displays hours and minutes (e.g., 0.00).
Example
Additional Tips
- Ensure that times are consistently entered in the same format.
- Double-check that the cells are formatted correctly for time calculations.
- If employees work overnight shifts, additional steps may be required to account for dates.
Following these steps, you can manually calculate hours worked in Excel or Google Sheets, including lunch breaks.
How Do You Calculate The Average Hours Worked Per Week?
If you need to manually calculate employee hours worked per week rather than per day, here’s what you should do:
- Consistent Hours: For employees with a fixed schedule, multiply the daily hours by the number of workdays. For example, if an employee works 8 hours and 15 minutes daily for 5 days a week: 8.25 hours/day × 5 days/week = 41.25 hours/week
- Variable Hours: For employees with varying daily hours, calculate the hours worked each day and total them for the week. Ensure that holidays, vacation days, or any time off are included.
Manual calculations can be complex and time-consuming. To simplify this process, consider using specialized online timesheet software like Avaza. These tools automate time tracking and billable & non-billable hour calculations, improving accuracy and efficiency.
Limitations Of Calculating Work Hours Manually
Manual work-hour tracking methods have significant drawbacks that impact accuracy, efficiency, and scalability for every type of business.
1. Human Error
Manual time tracking is prone to mistakes. Individuals might miscalculate, misrecord, or overlook critical data when recording hours by hand.
Simple errors like mistaking AM for PM or forgetting to log an entry can lead to inaccuracies in reported work hours. These errors can be costly, leading to incorrect payment calculations and potential disputes.
2. Time-Consuming
Tracking hours manually demands significant time and effort. Recording, calculating, and verifying work hours manually involves numerous steps, each susceptible to delays and inaccuracies.
This process diverts attention from critical tasks like project management and strategic planning. The repetitive nature of manual tracking consumes valuable resources, making it less efficient than automated systems like Avaza.
3. Scalability Issues
As a business expands, manual time tracking becomes increasingly impractical. Managing time records for a growing workforce involves handling a larger volume of data, which manual methods struggle to accommodate efficiently.
The complexity and volume of work hours increase, making it challenging to maintain accuracy and consistency.
Manual tracking cannot scale effectively for larger teams or organizations with complex time-tracking needs, leading to potential operational inefficiencies and increased administrative burdens.
What are Considered Work Hours?
Work hours refer to the time an employee spends performing their duties, on-site or remotely. This includes scheduled, paid, or contracted hours but excludes overtime for exempt employees.
Federal law requires accurate record-keeping for hourly, non-exempt, and exempt salaried employees. Records must detail daily hours worked, clock-in and clock-out times, breaks, overtime, and wages paid.
Compliance with DCAA (The Defense Contract Audit Agency) timekeeping requirements for government contractors involves tracking hours daily and maintaining records for at least two years.
Accurate tracking of work hours is essential for ensuring productivity and legal compliance.
Let’s explore the distinction between work and non-work hours to offer a thorough approach to effectively managing time.
‘Work Hours’ vs. ‘Non-Work Hours’
Work hours refer to the time an employee spends actively engaged in tasks assigned by the employer. The terms of employment typically define these hours.
Non-work hours include when the employee is not performing job-related tasks and is generally not compensated.
Understanding the difference between work and non-work hours is essential for accurate payroll and resource management. Here’s a breakdown of each with examples to clarify:
Scenario | Work Hours | Non-Work Hours |
Remote Work | Time spent actively working on tasks assigned by the employer, even if working from home. Example: An employee completing a report during their scheduled work hours. | Time spent on personal activities or breaks while at home, not related to work tasks. Example: An employee taking a lunch break during their remote workday. |
Job Training | Time spent attending mandatory training sessions is a requirement for the role. Example: A sales representative participating in a company-led webinar on new products. | Time spent on self-improvement or optional learning that the employer does not mandate. Example: An employee taking an evening course on personal development. |
Travel for Business | Time spent traveling to a client meeting or business event when it is part of the job duties. Example: A consultant travels to a client’s office for a meeting. | Time spent traveling between home and the office or on personal trips. Example: An employee driving to a worksite from their home. |
What Are The Different Types Of Work Hours?
Type of Work Hours | Description | Examples |
Part-time Hours | Hours worked that are less than full-time limits set by the employer. Part-time employees typically work fewer hours than their full-time counterparts. | Employees work 20 hours weekly in a retail store, while full-time employees work 40 hours. |
Full-time Hours | Hours worked that meet or exceed the employer’s definition of full-time work. Generally, full-time work involves 32-40 hours per week. | An office worker with a 40-hour workweek, or a company adopting a 4-day workweek with 32 hours. |
Overtime Hours | Hours worked beyond the standard full-time hours, typically over 44 hours per week. Overtime pay is usually higher, often time and a half. | An employee working 50 hours in a week, with 6 hours paid at an overtime rate of 1.5 times the regular pay. |
On-Call Hours | When employees are available to work if needed but are not actively working, on-call time may or may not be compensated, depending on company policies. | A technician can come to the office if an emergency arises but is not actively working unless called. |
Training Hours | Time spent on skill development or training required by the employer. If mandated by the company, training hours are typically considered work hours. | A nurse attending a workshop on new medical procedures during paid work time |
FAQs
How many hours is considered full-time?
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) does not provide a specific definition for full-time employment. Instead, the classification of full-time versus part-time work is determined by each employer. Generally, full-time employment is recognized as working 30 hours or more per week.
How many work hours are in a typical work week?
A standard full-time work week typically consists of 40 hours. Some employers may offer full-time positions with fewer hours, such as 32 hours per week.
How many work hours are in a year?
A typical full-time work year comprises 2,080 hours, calculated based on a 40-hour work week over 52 weeks.
Conclusion
Accurate time tracking is essential for businesses to ensure precise billing, efficient resource management, and compliance with legal requirements. However, manual calculations can be prone to errors, time-consuming, and challenging to scale as your business grows.
Online timesheet software offers a robust solution to these issues by automating time tracking, reducing human errors, and providing real-time reporting.
To find the best fit for your business, explore various options and choose software that aligns with your needs. Consider Avaza for a versatile and comprehensive solution.
Its user-friendly interface, real-time reporting, and seamless integration with accounting software make it a standout choice for optimizing time tracking, calculating hours worked, and invoicing.
